Courses Taught
|
ENV E 320 Designing Solutions for Environmental Problems
Description: Human interaction with the land, water and air environment; environmental pollution; role of engineering in solving environmental problems. Text: Environmental Science: Toward a Sustainable Future, Wright and Boorse, 13rd Ed. Videos of student projects: Avoiding single-use plastic in grocery packaging Salton Sea water quality improvement Bagasse alternative to single-use packaging |
|
ENV E 355 Environmental Engineering Description: Causes and effects of environmental problems and engineering methods to control them; introduction to Environmental Engineering. Text: Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science, Masters and Ela, 3rd Ed. How to work example problems and homework problems in this course (links to YouTube videos). ENV E 363 Environmental Engineering Laboratory Description: Analysis of natural waters and wastewaters, sampling and analysis of hazardous environmental pollutants, and techniques to analyze solid waste. Text: Chemistry for Environmental Engineering and Science by Sawyer, C.N., McCarty, P.L., Parkin, G.F., McGraw Hill, 5th edition, 2003. Service Learning in Spring 2016 through the SAGE Project. |
|
ENVE 445 Water and Wastewater Treatment
Description: Basic water chemistry, water quality criteria and standards, water usage and distribution. Biological, chemical, and physical processes to treat wastewater. Design of water and wastewater treatment unit processes. Potable and non-potable water reuse. Wastewater collection. Prerequisites: Environmental Engineering 355 and credit or concurrent registration in Civil Engineering 444. Text: no required text; course reader will be provided online. ENVE 555 Sustainable Water and Sanitation Systems
Description: Graduate and undergraduate level course in sustainable approaches to addressing local and global issues in water supply and sanitation. Topics covered include water supply, wastewater reuse and recovery, and solid waste management, and the course provides the engineering tools necessary to carry out basic design of water delivery, treatment, and sewage disposal systems in developing communities and rural communities in the US. Text: Field Guide to Environmental Engineering for Development Workers, Mihelcic et al., ASCE Press Students are encouraged to watch: Meet Mr. Toilet |
|
ENVE 645 Aquatic Chemistry for Environmental Engineers
Description: Graduate level course dealing with the chemistry of natural and polluted waters and its application in water and wastewater treatment. Students will learn and understand dilute aqueous solution chemistry of acid-base reactions, complex formations, precipitation and dissolution reactions, and oxidation-reduction recitations. ENV E 647 Physical & Chemical Processes for Water Pollution Control
Description: Engineering principles and design of physical and chemical processes used in water and wastewater treatment. Text: Water Treatment: Principles and Design, 3rd Ed., MWH. Crittenden et al. Field trip: Pure Water Demonstration Project for Indirect Potable Water Reuse. ENV E 648 Biological Processes and Bioremediation Engineering Description: Engineering principles and design of biological processes used in wastewater and bioremediation treatment technologies. Multiple textbooks and papers used. |
|
PREVIOUS:
CE 563 Environmental Engineering Fundamentals Description: Basic physical, chemical, and biological concepts and the applications to the protection of the environment with emphasis on techniques used in water and wastewater treatment. Text: Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science, Masters and Ela, 3rd Ed. |
|
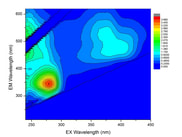
CE 816 Natural Organic Matter Characterization and Modeling Description: Graduate level course in characterization and modeling of natural organic matter (NOM) in natural and polluted aquatic environments. Covers principles of optical spectroscopy, parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) modeling, and recent advances in tracking dissolved organic matter sources and transformations. Text: assigned readings |